Volume 7, Issue 4 (November 2020)
Avicenna J Neuro Psycho Physiology 2020, 7(4): 204-210 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Ghavidel A, Sahebalzamani M, Gholi Ghorchian N, Zamani Moghadam A. Attitude Modeling, Job Similarity and Information Structure in Faculty Members. Avicenna J Neuro Psycho Physiology 2020; 7 (4) :204-210
URL: http://ajnpp.umsha.ac.ir/article-1-255-en.html
URL: http://ajnpp.umsha.ac.ir/article-1-255-en.html
1- Ph.D. Candidate in Educational Management, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
2- Associate Professor, Tehran Medical Science, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran ,m_szamani@iautmu.ac.ir
3- Professor, Faculty of Management and Economics, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
4- Associate Professor, School of Management and Economics, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
2- Associate Professor, Tehran Medical Science, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran ,
3- Professor, Faculty of Management and Economics, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
4- Associate Professor, School of Management and Economics, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
Full-Text [PDF 552 kb]
(1239 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3640 Views)
Table 1. Single-sample t-test results to assess the current situation of faculty member workload dimensions (n=230)
Table 2. Results of the dependent t-test to compare the current and optimal situation of the faculty member workload dimensions


Full-Text: (1699 Views)
Background
Higher education has been considered a focal point that guarantees the progression of society in the political, social, cultural, economic, and other fields ]1[. In most developed countries and developing countries, the solutions to problems and fulfillment of the needs of national development goals have been realized by universities and academics ]2[. The superiority of human resources and social capital in the production of science indicates the necessity of making changes in line with global changes in education and research in a country to achieve the above position]3[.
Today, faculty members work in environments where complex activities are required] 4[. However, today's situation has changed in such a way that based on the defined workload, many expectations of faculty members are met and their performance in this regard is often evaluated ]5[. Therefore, knowledge of the factors affecting job satisfaction can lead to a happier environment for individuals ]6[. Many factors affect the job satisfaction of faculty members, one of the most important of which is workload ]7[. Professors must perform more research than just teaching so that they can successfully fulfill their job commitments ]8[. The faculty members are the central sources around whom the process and results of higher education revolve ]9[.
Due to an increase in the need for higher education and units in the Islamic Azad University along with constraints in financial resources in this university, it is necessary to develop a workload program that is applicable, flexible, and compatible with academic and local conditions.
On the other hand, due to increasing changes in science and technology, it is necessary to periodically evaluate the workload of faculty members of universities to provide basic steps to improve the quality of education, provide opportunities for growth and development in faculty members, and establish justice.
Job satisfaction of the faculty members should be determined, followed by the identification of the real workload of the faculty members in higher education institutions, especially the Islamic Azad University. Accordingly, measures can be taken to allocate productive and fair time for faculty members.
When professors are acquainted with the workload, the university presidents can increase their efforts to strengthen their scientific, research, and cultural strength. Moreover, they will be able to participate in conferences, workshops, as well as scientific and entrepreneurial seminars.
It is of utmost importance to help the senior managers of the Azad Universities raise the awareness of the professors to create an active environment in the realm of teaching and enrichment of the students at these universities.
Objectives
This study aimed to provide a model for determining the faculty member workload at Hamadan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamadan, Iran.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted based on an applied research method using quantitative and qualitative data. The data were collected through interviews and a workload questionnaire. This study can be considered a kind of exploratory research, and the researcher intends to present a model that can be presented under the research indicators in this way.
The present study includes three different phases. In order to determine the sample size of the qualitative part of the research, a purposeful non-random method was used which was continued until the theoretical saturation of the interview. A total of 15 interviews were performed, and the statistical population of the quantitative part included all full-time and part-time faculty members at Hamadan Branch, Azad Universities, Hamadan, Iran in the academic year 2018-19. During the study, the number of faculty members was determined at 388 cases who were selected using the stratified random method. Eventually, the sample size was estimated at 230 individuals to increase the accuracy of the results.
Closed Questionnaire
The first section of this scale seeks demographic characteristics that cover such information as gender, age, marital status, and education level. Furthermore, the components and sub-components obtained from the theoretical literature and interviews were classified into seven dimensions in the second section. The scores are rated on a 5-point Likert scale.
Lasheh method was utilized in order to determine the validity of this questionnaire. Moreover, quantitative content validity, two relative content validity coefficients (CVR), and content validity index (CVI) were used to evaluate the validity of the content.
Considering the Lavosheh method ]11[, it can be stated that in this method, according to the standard table of Lavosheh, the number of experts has been determined, and the minimum value of the narrative should be selected according to the number of experts.
According to the above explanations, the questionnaire was given to 10 professors and experts in the field of human resource management to determine validity [1]. The minimum validity value must be above 0.62 in order to obtain the reliability of the confidence questionnaire.
Where ne is the number of specialists who have answered the "necessary" option and N signifies the total number of specialists. If the calculated value is greater than the table value, the content validity of that item is accepted.

Equation 1. Content Validity Coefficient Index Formula
Furthermore, the minimum acceptable value for the CVI index is 0.79, and if the CVI index is less than 0.79, it should be reviewed in the questionnaire]12[, which requires a serious revision given the range of responses (unrelated).
The results showed that the calculated value was equal to 0.92, which was more than 0.79. Therefore, its narrative index was also confirmed. According to the research method applied in this study, the data were analyzed in SPSS and PLS software. In the qualitative analysis dimension, content analysis was used using semi-structured interviews to identify the most important criteria for modeling the workload of faculty members.
Krippendorf introduces content analysis as a research method used to duplicate and validate inferences from data about their text]13[. He considers the purpose of this analysis, the same as other research techniques, to provide cognition, new insight, image of reality, and a guide to action, which includes the three main steps of open coding, central coding, and code selection.
In the quantitative part of the research, the developed questionnaire, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, as well as structural equation modeling were used to evaluate the relationships in presenting the model for faculty member workload determination. The reliability of the questionnaire was assessed using Cronbach's alpha coefficient and compound reliability by Smart-PLS statistics. Moreover, the results were presented separately for each variable.
Results
The present study was conducted based on a qualitative-quantitative research method. In this study, the collected data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistical indicators, such as frequency tables of demographic characteristics of the subjects were examined at the descriptive level. Regarding the inferential statistics, related statistical tests, including exploratory factor analysis and sample t-test were used to determine the components of the model and examine the current situation, respectively. In addition, structural equation modeling was used to validate and fit the model. Moreover, the gap between the current and the desired situation was examined using the paired t-test in order to provide a solution.
If the findings of the table show the descriptive
indicators of the extracted dimensions, in the current situation, the lowest mean is related to "entrepreneurship" (2.16), and the highest mean related to "design" (3.51). In the optimal situation, the lowest mean is related to "culture" (4.21), and the highest mean is related to "individual development" (4.74) since the questions are rated on a 5-point Likert scale from (very low=1) to (very high=5). In fact, the middle number in the above range is three. This finding indicates that according to the respondents, the dimension of the faculty member workload at the Islamic Azad Universities of Hamadan province, Iran, in the desired situation is higher than the average.
Furthermore, regarding the skewness degree and elongation of the dimensions, the dimension and elongation of the existing and desired conditions of the skeleton are in the range from +2 to -2; accordingly, there is no violation of the normality in the data. Therefore, parametric tests can be used to analyze existing research data.
In this section, the research questions are examined using related statistical tests, including a sample t-test to determine the status of the variables, a dependent t-test to compare the status quo, desirable and exploratory factor analysis (analysis of the main component), and confirmatory factor analysis. Structural equation modeling has been used through LISREL software.
As shown in Table 1, there is a significant difference between the observed "design" and the theoretical average of the scale (expected average) (P<0.05 and t=7.903) since its significance level is less than 0.05. Therefore, the observed average "design" (3.52) is higher than the expected average (score 3). This means that the current state of "design" is above average.
As can be seen in Table 2, there is a significant difference between the observed "design" in the current situation and the desired situation (P<0.05, t=16.251) since its significance level is less than
Today, faculty members work in environments where complex activities are required] 4[. However, today's situation has changed in such a way that based on the defined workload, many expectations of faculty members are met and their performance in this regard is often evaluated ]5[. Therefore, knowledge of the factors affecting job satisfaction can lead to a happier environment for individuals ]6[. Many factors affect the job satisfaction of faculty members, one of the most important of which is workload ]7[. Professors must perform more research than just teaching so that they can successfully fulfill their job commitments ]8[. The faculty members are the central sources around whom the process and results of higher education revolve ]9[.
Due to an increase in the need for higher education and units in the Islamic Azad University along with constraints in financial resources in this university, it is necessary to develop a workload program that is applicable, flexible, and compatible with academic and local conditions.
On the other hand, due to increasing changes in science and technology, it is necessary to periodically evaluate the workload of faculty members of universities to provide basic steps to improve the quality of education, provide opportunities for growth and development in faculty members, and establish justice.
Job satisfaction of the faculty members should be determined, followed by the identification of the real workload of the faculty members in higher education institutions, especially the Islamic Azad University. Accordingly, measures can be taken to allocate productive and fair time for faculty members.
When professors are acquainted with the workload, the university presidents can increase their efforts to strengthen their scientific, research, and cultural strength. Moreover, they will be able to participate in conferences, workshops, as well as scientific and entrepreneurial seminars.
It is of utmost importance to help the senior managers of the Azad Universities raise the awareness of the professors to create an active environment in the realm of teaching and enrichment of the students at these universities.
Objectives
This study aimed to provide a model for determining the faculty member workload at Hamadan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Hamadan, Iran.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted based on an applied research method using quantitative and qualitative data. The data were collected through interviews and a workload questionnaire. This study can be considered a kind of exploratory research, and the researcher intends to present a model that can be presented under the research indicators in this way.
The present study includes three different phases. In order to determine the sample size of the qualitative part of the research, a purposeful non-random method was used which was continued until the theoretical saturation of the interview. A total of 15 interviews were performed, and the statistical population of the quantitative part included all full-time and part-time faculty members at Hamadan Branch, Azad Universities, Hamadan, Iran in the academic year 2018-19. During the study, the number of faculty members was determined at 388 cases who were selected using the stratified random method. Eventually, the sample size was estimated at 230 individuals to increase the accuracy of the results.
Closed Questionnaire
The first section of this scale seeks demographic characteristics that cover such information as gender, age, marital status, and education level. Furthermore, the components and sub-components obtained from the theoretical literature and interviews were classified into seven dimensions in the second section. The scores are rated on a 5-point Likert scale.
Lasheh method was utilized in order to determine the validity of this questionnaire. Moreover, quantitative content validity, two relative content validity coefficients (CVR), and content validity index (CVI) were used to evaluate the validity of the content.
Considering the Lavosheh method ]11[, it can be stated that in this method, according to the standard table of Lavosheh, the number of experts has been determined, and the minimum value of the narrative should be selected according to the number of experts.
According to the above explanations, the questionnaire was given to 10 professors and experts in the field of human resource management to determine validity [1]. The minimum validity value must be above 0.62 in order to obtain the reliability of the confidence questionnaire.
Where ne is the number of specialists who have answered the "necessary" option and N signifies the total number of specialists. If the calculated value is greater than the table value, the content validity of that item is accepted.

Equation 1. Content Validity Coefficient Index Formula
Furthermore, the minimum acceptable value for the CVI index is 0.79, and if the CVI index is less than 0.79, it should be reviewed in the questionnaire]12[, which requires a serious revision given the range of responses (unrelated).
The results showed that the calculated value was equal to 0.92, which was more than 0.79. Therefore, its narrative index was also confirmed. According to the research method applied in this study, the data were analyzed in SPSS and PLS software. In the qualitative analysis dimension, content analysis was used using semi-structured interviews to identify the most important criteria for modeling the workload of faculty members.
Krippendorf introduces content analysis as a research method used to duplicate and validate inferences from data about their text]13[. He considers the purpose of this analysis, the same as other research techniques, to provide cognition, new insight, image of reality, and a guide to action, which includes the three main steps of open coding, central coding, and code selection.
In the quantitative part of the research, the developed questionnaire, exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis, as well as structural equation modeling were used to evaluate the relationships in presenting the model for faculty member workload determination. The reliability of the questionnaire was assessed using Cronbach's alpha coefficient and compound reliability by Smart-PLS statistics. Moreover, the results were presented separately for each variable.
Results
The present study was conducted based on a qualitative-quantitative research method. In this study, the collected data were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistical indicators, such as frequency tables of demographic characteristics of the subjects were examined at the descriptive level. Regarding the inferential statistics, related statistical tests, including exploratory factor analysis and sample t-test were used to determine the components of the model and examine the current situation, respectively. In addition, structural equation modeling was used to validate and fit the model. Moreover, the gap between the current and the desired situation was examined using the paired t-test in order to provide a solution.
If the findings of the table show the descriptive
indicators of the extracted dimensions, in the current situation, the lowest mean is related to "entrepreneurship" (2.16), and the highest mean related to "design" (3.51). In the optimal situation, the lowest mean is related to "culture" (4.21), and the highest mean is related to "individual development" (4.74) since the questions are rated on a 5-point Likert scale from (very low=1) to (very high=5). In fact, the middle number in the above range is three. This finding indicates that according to the respondents, the dimension of the faculty member workload at the Islamic Azad Universities of Hamadan province, Iran, in the desired situation is higher than the average.
Furthermore, regarding the skewness degree and elongation of the dimensions, the dimension and elongation of the existing and desired conditions of the skeleton are in the range from +2 to -2; accordingly, there is no violation of the normality in the data. Therefore, parametric tests can be used to analyze existing research data.
In this section, the research questions are examined using related statistical tests, including a sample t-test to determine the status of the variables, a dependent t-test to compare the status quo, desirable and exploratory factor analysis (analysis of the main component), and confirmatory factor analysis. Structural equation modeling has been used through LISREL software.
As shown in Table 1, there is a significant difference between the observed "design" and the theoretical average of the scale (expected average) (P<0.05 and t=7.903) since its significance level is less than 0.05. Therefore, the observed average "design" (3.52) is higher than the expected average (score 3). This means that the current state of "design" is above average.
As can be seen in Table 2, there is a significant difference between the observed "design" in the current situation and the desired situation (P<0.05, t=16.251) since its significance level is less than
Table 1. Single-sample t-test results to assess the current situation of faculty member workload dimensions (n=230)
| Variables | Expected average=3 | |||||
| X | SD | MD | T | df | sig | |
| Design | 3.52 | 0.99 | 0.51 | 7.903 | 229 | 0.000 |
| Run | 3.46 | 0.77 | 0.46 | 9.105 | 229 | 0.000 |
| Evaluation | 3.13 | 0.88 | 0.13 | 2.236 | 229 | 0.026 |
| Training and teaching | 3.37 | 0.84 | 0.37 | 6.678 | 229 | 0.000 |
| Research at university | 2.55 | 0.94 | 0.45 - | -7.256 | 229 | 0.000 |
| External research out of university | 2.42 | 0.87 | -0.58 | - 10.147 | 229 | 0.000 |
| Research | 2.49 | 0.87 | 0.51 - | 8.927 - | 229 | 0.000 |
| Consultation | 2.99 | 0.88 | 0.009 - | 0.153 - | 229 | 0.879 |
| Executive and managerial activities | 2.83 | 0.77 | -0.17 | -3.297 | 229 | 0.001 |
| Individual development | 3.19 | 0.89 | 0.19 | 3.208 | 229 | 0.002 |
| Extracurricular activities | 2.65 | 0.86 | 0.35 - | 6.128 - | 229 | 0.000 |
| Entrepreneurship | 2.16 | 0.86 | 0.84 - | 14.905 - | 229 | 0.000 |
| Culture | 2.45 | 1.03 | 0.55 - | 8.049 - | 229 | 0.000 |
| Services | 2.71 | 0.73 | 0.29- | 6.017 - | 229 | 0.000 |
0.05. Accordingly, the average desired "design" situation (4.57) is higher than the current average (3.52). This means that the current "design" situation is unfavorable.
In order to present, test, and confirm the workload model for faculty members, the structural equation modeling technique has been used for the second-order factor analysis model using the LISREL software package (Figure 1).
Given that all t-statistical values of the paths are greater than 1.96 (Figure 2), there is a significant
relationship between each dimension and the faculty member workload. The table 3 tabulates the fit indicators of the second-factor analysis model for the faculty member workload.
The obtained results reveal a good fitness of the model. This marking simply indicates whether they have received a powerful, free, and intermediate model of presence. The Chi-square test result shows an established consensus between the sample quadrilateral matrix and the covariance matrix (community).
In order to present, test, and confirm the workload model for faculty members, the structural equation modeling technique has been used for the second-order factor analysis model using the LISREL software package (Figure 1).
Given that all t-statistical values of the paths are greater than 1.96 (Figure 2), there is a significant
relationship between each dimension and the faculty member workload. The table 3 tabulates the fit indicators of the second-factor analysis model for the faculty member workload.
The obtained results reveal a good fitness of the model. This marking simply indicates whether they have received a powerful, free, and intermediate model of presence. The Chi-square test result shows an established consensus between the sample quadrilateral matrix and the covariance matrix (community).
Table 2. Results of the dependent t-test to compare the current and optimal situation of the faculty member workload dimensions
| Sig. | df | t | differences in averages | Average optimal situation | Average current situation | Dimensions |
| 0.000 | 229 | -16.251 | -1.05 | 4.57 | 3.52 | Design |
| 0.000 | 308 | -12.261 | -0.80 | 4.27 | 3.46 | Run |
| 0.000 | 308 | -26.00 | -1.50 | 4.63 | 3.13 | Evaluation |
| 0.000 | 308 | -20.058 | -1.12 | 4.49 | 3.37 | Training and teaching |
| 0.000 | 308 | -32.118 | -2.08 | 4.63 | 2.55 | Research at university |
| 0.000 | 229 | -32.941 | -2.05 | 4.47 | 2.42 | External research out of university |
| 0.000 | 229 | -34.470 | -2.06 | 4.56 | 2.49 | Research |
| 0.000 | 229 | -26.008 | -1.59 | 4.58 | 2.99 | Consultation |
| 0.000 | 229 | -25.819 | -1.47 | 4.31 | 2.83 | Executive and managerial activities |
| 0.000 | 229 | -27.192 | -1.55 | 4.74 | 3.19 | Individual development |
| 0.000 | 229 | -29.606 | -1.81 | 4.46 | 2.65 | Extracurricular activities |
| 0.000 | 229 | -34.468 | -2.14 | 4.29 | 2.16 | Entrepreneurship |
| 0.000 | 229 | -25.146 | -1.76 | 4.22 | 2.45 | Culture |
| 0.000 | 229 | -35.419 | -1.72 | 4.43 | 2.71 | Services |

Figure 1. Confirmatory factor analysis workload model for faculty members in the standard estimation mode

Figure 2. Second-order factor analysis workload model for faculty members in a meaningful manner
Table 3. Fitness indicators of the general model for faculty member workload
| Limit | Estimates | Component name |
| P>0.05 | 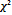 |
 |
| 40=df | ||
| >0.05 | 1.84 |  |
| >0.08 | 0.061 | Average square root of RMSEA estimation error |
| <0.09 | 0.94 | Good fit GFI |
| <0.09 | 0.91 | AGFI modified fitness goodness |
| <0.09 | 0.95 | Softened NFI shedding |
| <0.09 | 0.97 | Non-softened NNFI |
| >0.05 | 0.045 | The root of the mean squares remaining the standard SRMR |
| <0.09 | 0.98 | Comparative CFI Failure |
RMSEA: Root Mean Square Error of Approximation
GFH: Goodness-of-Fit Index
AGFI: Adjusted-Goodness-of-Fit Index
NFI: Normed Fit Index
NNFI: Non-normed fit index
SRMR: Standardized Root Mean Squared Error
CFI: comparative fit index
According to the above table, the chi-square value with a degree of freedom of 40 was obtained at 73.67. Moreover, its significance level was estimated at 0.000, which was statistically significant at 0.05. Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected in this study.
Summary of the result
As shown in Table 3, there is a significant difference between the mean of the model presented in all dimensions and the expected mean at the error level of 5% (P<0.05). Therefore, the null hypothesis of no difference between the observed mean and the mean of the community (3) is rejected, and a significant difference is found between the observed mean and the mean of the community (3). Therefore, the presented model was approved by 95% of the experts regarding the dimensions, such
as "Philosophy" (4.00), "Objectives" (04.04), "Theoretical Foundations" (4.17), "Dimensions and Components of Workload" (4.02), "Mechanisms and Executive" (4.99), as well as "Feedback, Correction, Evaluation, and Reengineering system "(4.14).
Discussion
The present study aimed to provide a model to determine the faculty member workload dimensions at the Islamic Azad University, Hamadan Branch, Hamadan, Iran. The dimensions were classified into seven categories of "education and teaching", "research", "specialized activities outside university", "entrepreneurship dimensions", "individual develop-pment", "culture" and "other activities".
Executive and managerial sub-categories of each dimension formed the dimensions of the model. Moreover, it was determined by fitting the model that the proposed scheme could be used as a desirable model to determine the professors' workload. It is a set of specific categories of measurement of responsibilities. The workload is measured as total activities, such as the amount of contact with faculty members in the classroom
Higher education institutions play an important role in the sustainable development of societies. The professional development of faculty members is
the key to improving the quality of higher education]11[.
Universities account for success in three functional areas of education, research, and service delivery to society. Accordingly, they should pay attention to strengthening the abilities of the members of the scientific board. The strengthening of these abilities will be achieved through their professional development and maturity. A look at the frequency distribution of faculty members according to their academic rank at Azad Universities in Iran also confirms the necessity of developing programs for the professional development of faculty members ]12[.
Therefore, universities must pay attention to determining the appropriate workload along with educational and research activities. Many professors also pay attention to the entrepreneurship dimension, as well as executive and managerial activities, which ultimately improve their job performance and students' education.
Bahrami et al.]13[ stated that an increase in the number of counseling sessions and student guidance can be effective in improving the performance of supervisors. It is also recommended that professors professionally provide guidance and counseling. Similarly, Mirshah Jafari et al. ]14[ obtained different results from the two approaches of student evaluation and teacher self-assessment in examining the effective teaching performance of faculty members.
According to a study conducted by Rastegari et al.]15[, the components of job performance were educational, research, professional, and individual competencies.
According to the identified components, it is suggested that the rules and regulations related to the promotion of teachers' job performance be reviewed and amended ]16-20[.
In the same vein, Basaroudin et al. ]21-23[ in a study entitled "A quantitative model to determine the workload of faculty members" indicated that attention to "teaching", "research", and "develop-mental activities" were the main dimensions of the model, which should be considered according to the importance of each appropriate hour. It should be noted that the majority of the hours are suitable for teaching activities, and the least useful hours are allocated to research]24, 25[.
Regarding the limitations of this study, one can name the study setting which was limited to Hamadan province, Iran; therefore, the results cannot be generalized beyond that particular group, and the proposed model is merely applied to the current situation. Furthermore, there is the probability of an error affecting the respondents, including the ease of error in which individuals consider too many degrees and scores. Accordingly, they get either a tendency to focus on the center, which makes people tend to have moderate grades and scores in the questionnaire that cannot be controlled.
Therefore, it is recommended that further studies be conducted to identify the obstacles to the implementation of the recommendations of this study. Moreover, the present study should be replicated in public universities to compare the results focusing on the faculty member workload using methods, such as the analytical hierarchy process to determine the priority of each of the main dimensions and sub-components of the model.
Conclusions
It can be concluded that Azad Universities of Hamadan province, Iran, have not yet been able to consider appropriate activities for faculty members in the main categories of "research", "entrepre-neurship", "individual development", "culture", and "other activities" that professors pay attention to. On the other hand, the main focus is on "teaching and learning" and "executive activities".
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of the study
References
GFH: Goodness-of-Fit Index
AGFI: Adjusted-Goodness-of-Fit Index
NFI: Normed Fit Index
NNFI: Non-normed fit index
SRMR: Standardized Root Mean Squared Error
CFI: comparative fit index
According to the above table, the chi-square value with a degree of freedom of 40 was obtained at 73.67. Moreover, its significance level was estimated at 0.000, which was statistically significant at 0.05. Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected in this study.
Summary of the result
As shown in Table 3, there is a significant difference between the mean of the model presented in all dimensions and the expected mean at the error level of 5% (P<0.05). Therefore, the null hypothesis of no difference between the observed mean and the mean of the community (3) is rejected, and a significant difference is found between the observed mean and the mean of the community (3). Therefore, the presented model was approved by 95% of the experts regarding the dimensions, such
as "Philosophy" (4.00), "Objectives" (04.04), "Theoretical Foundations" (4.17), "Dimensions and Components of Workload" (4.02), "Mechanisms and Executive" (4.99), as well as "Feedback, Correction, Evaluation, and Reengineering system "(4.14).
Discussion
The present study aimed to provide a model to determine the faculty member workload dimensions at the Islamic Azad University, Hamadan Branch, Hamadan, Iran. The dimensions were classified into seven categories of "education and teaching", "research", "specialized activities outside university", "entrepreneurship dimensions", "individual develop-pment", "culture" and "other activities".
Executive and managerial sub-categories of each dimension formed the dimensions of the model. Moreover, it was determined by fitting the model that the proposed scheme could be used as a desirable model to determine the professors' workload. It is a set of specific categories of measurement of responsibilities. The workload is measured as total activities, such as the amount of contact with faculty members in the classroom
Higher education institutions play an important role in the sustainable development of societies. The professional development of faculty members is
the key to improving the quality of higher education]11[.
Universities account for success in three functional areas of education, research, and service delivery to society. Accordingly, they should pay attention to strengthening the abilities of the members of the scientific board. The strengthening of these abilities will be achieved through their professional development and maturity. A look at the frequency distribution of faculty members according to their academic rank at Azad Universities in Iran also confirms the necessity of developing programs for the professional development of faculty members ]12[.
Therefore, universities must pay attention to determining the appropriate workload along with educational and research activities. Many professors also pay attention to the entrepreneurship dimension, as well as executive and managerial activities, which ultimately improve their job performance and students' education.
Bahrami et al.]13[ stated that an increase in the number of counseling sessions and student guidance can be effective in improving the performance of supervisors. It is also recommended that professors professionally provide guidance and counseling. Similarly, Mirshah Jafari et al. ]14[ obtained different results from the two approaches of student evaluation and teacher self-assessment in examining the effective teaching performance of faculty members.
According to a study conducted by Rastegari et al.]15[, the components of job performance were educational, research, professional, and individual competencies.
According to the identified components, it is suggested that the rules and regulations related to the promotion of teachers' job performance be reviewed and amended ]16-20[.
In the same vein, Basaroudin et al. ]21-23[ in a study entitled "A quantitative model to determine the workload of faculty members" indicated that attention to "teaching", "research", and "develop-mental activities" were the main dimensions of the model, which should be considered according to the importance of each appropriate hour. It should be noted that the majority of the hours are suitable for teaching activities, and the least useful hours are allocated to research]24, 25[.
Regarding the limitations of this study, one can name the study setting which was limited to Hamadan province, Iran; therefore, the results cannot be generalized beyond that particular group, and the proposed model is merely applied to the current situation. Furthermore, there is the probability of an error affecting the respondents, including the ease of error in which individuals consider too many degrees and scores. Accordingly, they get either a tendency to focus on the center, which makes people tend to have moderate grades and scores in the questionnaire that cannot be controlled.
Therefore, it is recommended that further studies be conducted to identify the obstacles to the implementation of the recommendations of this study. Moreover, the present study should be replicated in public universities to compare the results focusing on the faculty member workload using methods, such as the analytical hierarchy process to determine the priority of each of the main dimensions and sub-components of the model.
Conclusions
It can be concluded that Azad Universities of Hamadan province, Iran, have not yet been able to consider appropriate activities for faculty members in the main categories of "research", "entrepre-neurship", "individual development", "culture", and "other activities" that professors pay attention to. On the other hand, the main focus is on "teaching and learning" and "executive activities".
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of the study
References
- Salehi Omran E, Einkhah F, Barani S. Investigating the position of skill learning in the comprehensive scientific map of Iran. Iranian Higher Education. 2019; 11(1):1-38.
- Kiaie TN, Zeinabadi HR, Arasteh HR, Abbassian H. Reflection on the effective causes of research malfunctions in Iranian universities and higher education institutions. Iranian Higher Education. 2019; 11(1):39-66.
- Taher Tolou Del MS, Kamali Tabrizi S, Heydaripour O. Investigating the educational capabilities of virtual reality technology based on the evaluation of visual perception components. Iranian Higher Education. 2019; 11(1):161-99.
- Bahrami S, Rajaeepour S, Aghahosseni T, Bakhtiar Nasrabadi HA, Yarmohamadian MH. Analysis of multiple relationships of intellectual capital and organizational innovation in higher education. Quarterly Journal of Research and Planning in Higher Education. 2011; 17(3):27-50.
- Enayati NA, Uosefi M, Siyami L, Javaheri DM. Evaluation of the quality of education services of Payam Noor University of Hamedan based on the SERVQUAL Model. Journal of Research and Planning in Higher Education. 2011; 17(3):135-51.
- Lee EU. The eco-club: a place for the becoming active citizen? Environmental Education Research. 2017; 23(4):515-32. [DOI:10.1080/13504622.2016.1149552]
- Howe C, Mercer N. Commentary on the papers. Language and Education. 2017; 31(1):83-92. [DOI:10.1080/095
00782.2016.1230126] - Pérez-Paredes P, Jiménez PA, Hernández PS. Constructing immigrants in UK legislation and Administration informative texts: a corpus-driven study (2007–2011). Discourse & Society. 2017; 28(1):81-103. [DOI:10.1177/09579265
16676700] - Teperek M, Morgan R, Ellefson M, Kingsley D. Starting from the end: what to do when restricted data is released. Data Science Journal. 2017; 16(4):1-11. [DOI:10.5334/dsj-2017-010]
- Hennessy S, Rojas-Drummond S, Higham R, Márquez AM, Maine F, Ríos RM, et al. Developing a coding scheme for analysing classroom dialogue across educational contexts. Learning, Culture and Social Interaction. 2016; 9:16-44. [DOI:10.1016/j.lcsi.2015.12.001]
- Vignoles A, Murray N. Widening participation in higher education. Education Sciences. 2016; 6(2):13. [DOI:10.3390/
educsci6020013] - Warwick P, Vrikki M, Vermunt JD, Mercer N, van Halem N. Connecting observations of student and teacher learning: an examination of dialogic processes in Lesson Study discussions in mathematics. ZDM Mathematics Education. 2016; 48(4):555-69. [DOI:10.1007/s11858-015-0750-z]
- Dillabough JA. Education, work and identity: Themes and perspectives. Journal of Education Policy. 2016; 31(5):678-80. [DOI:10.1080/02680939.2016.1143253]
- Sriprakash A, Qi J, Singh M. The uses of equality in an elite school in India: enterprise and merit. British Journal
of Sociology of Education. 2017; 38(7):1022-36. [DOI:10.1080/01425692.2016.1218754] - Cremin H, Guilherme A. Violence in schools: perspectives (and hope) from galtung and buber. Educational Philosophy and Theory. 2016; 48(11):1123-37. [DOI:10.1080/00
131857.2015.1102038] - Wegerif R, Fujita T, Doney J, Linares JP, Richards A, Van Rhyn C. Developing and trialing a measure of group thinking. Learning and Instruction. 2017; 48:40-50. [DOI:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2016.08.001]
- Takayama K, Sriprakash A, Connell R. Toward a postcolonial comparative and international education. Comparative Education Review. 2017; 61(S1):S1-24. [DOI: 10.1086/690455]
- Cornelissen F, McLellan RW, Schofield J. Fostering research engagement in partnership schools: Networking and value creation. Oxford Review of Education. 2017; 43(6):695-717. [DOI:10.1080/03054985.2017.1316251]
- Dillabough JA, Yoon ES. Youth geographies of urban estrangement in the Canadian city: risk management, race relations and the ‘sacrificial stranger’. Children's Geographies. 2018; 16(2):128-42. [DOI: 10.1080/14733285.
2017.1334113] - Després JP, Burnard P, Dubé F, Stévance S. Expert western classical music improvisers’ strategies. Journal of Research in Music Education. 2017; 65(2):139-62. [DOI: 10.1177/00224294177107 77]
- Hoare L. “The school career of the child as a unity”: John Newsom’s involvement with the BBC, 1934–1971. Paedagogica Historica. 2017; 53(4):411-27. [DOI:10.1080/
00309230.2016.1273247] - Yakavets N, Frost D, Khoroshash A. School leadership and capacity building in Kazakhstan. International Journal
of Leadership in Education. 2017; 20(3):345-70. [DOI:10.1080/ 13603124.2015.1066869] - Taber KS. Always a matter of interpretation: inferring student knowledge and understanding from research data. Chemistry Education Research and Practice. 2017; 18(1):7-12. [DOI:10.1039/C6RP90012G]
- Casanova D, Moreira A. A model for discussing the quality of technology-enhanced learning in blended learning programmes. Online Course Management: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications, Aveiro, Portugal; 2018. P. 184-204. [DOI: 10.4018/978-1-5225-5472-1.ch010]
- Abdellatief M, Sultan AB, Jabar MA, Abdullah R. A technique for quality evaluation of e-learning from developers perspective. American Journal of Economics
and Business Administration. 2011; 3(1):157-64. [DOI:10.3844/ajebasp.2011.157.164]
Article Type: Research Article |
Subject:
General
Received: 2020/04/15 | Accepted: 2020/06/2 | Published: 2020/11/16
Received: 2020/04/15 | Accepted: 2020/06/2 | Published: 2020/11/16
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |







